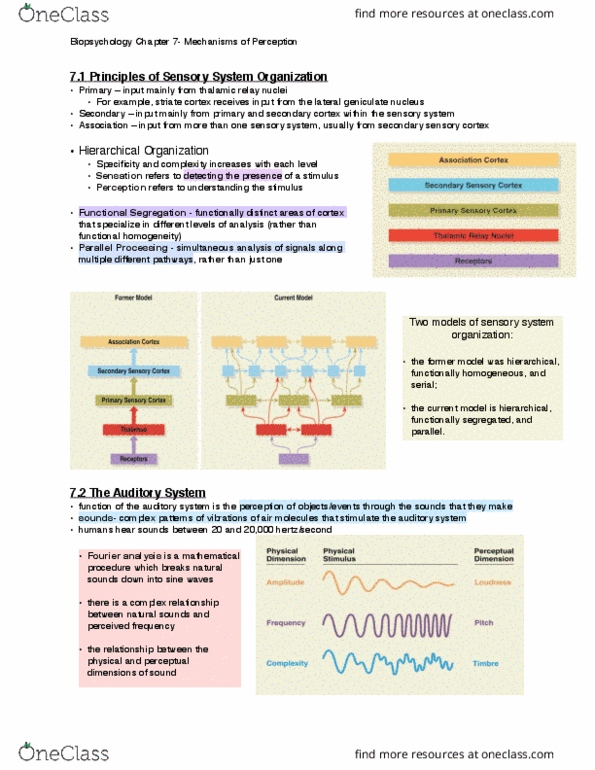
The Thalamic Relay Nucleus For The Auditory System Is The
The thalamic relay nucleus for the auditory system is the. In the auditory forebrain center field L and the auditory portions of the hyperstriatum ventrale up to 8 of the cells were immunopositive. The first relay in common with the primary auditory pathway locates in the cochlear nuclei brainstem. Together with the lateral geniculate body which is the relay station of the optic system it constitutes the metathalamus.
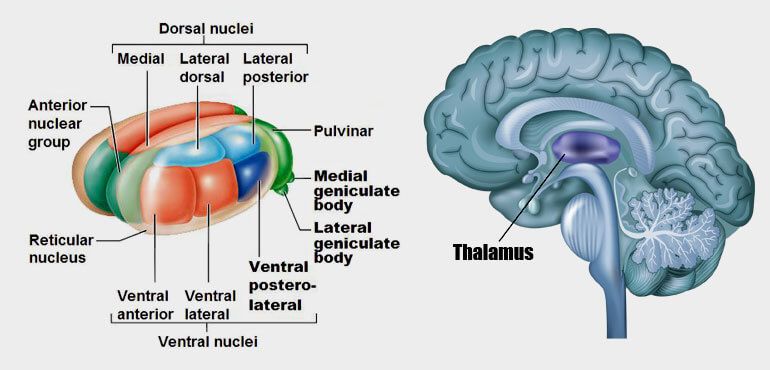
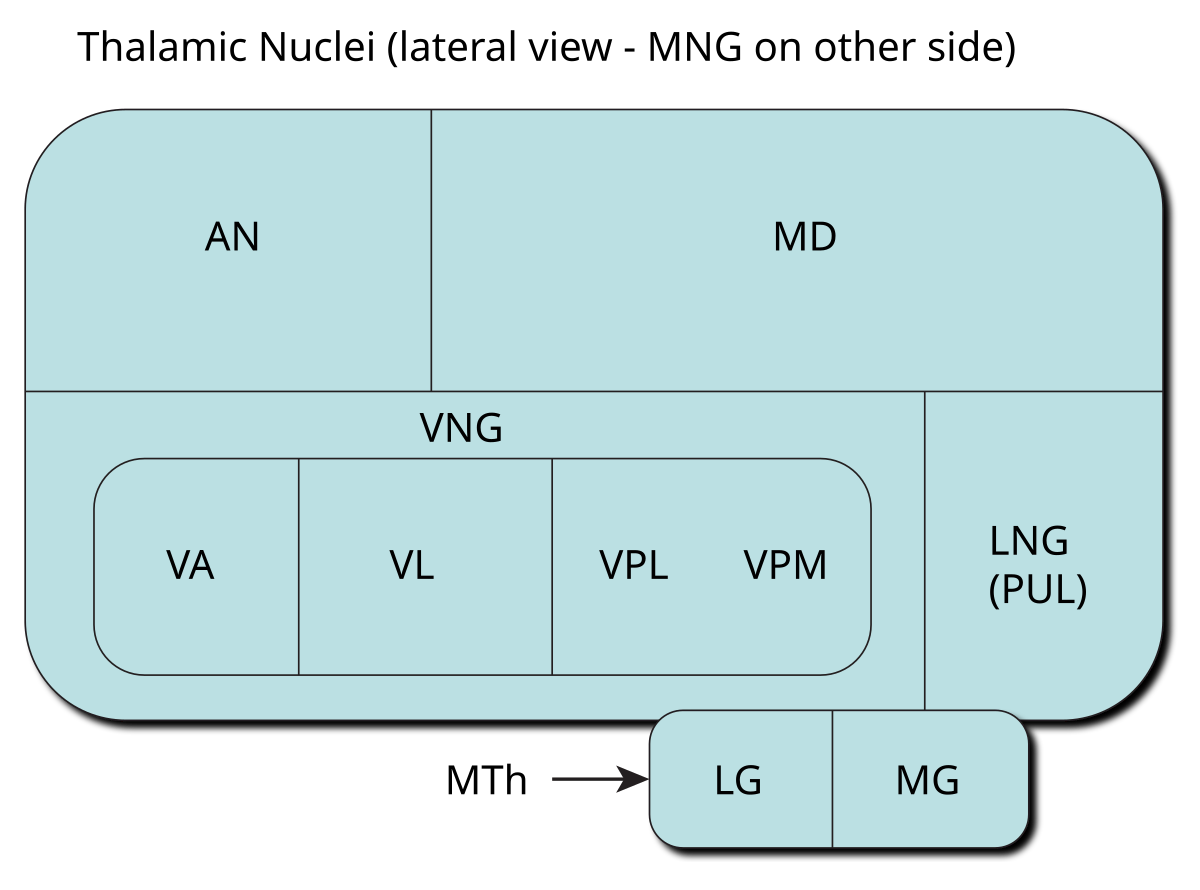
The metathalamus consists of two oval eminences the geniculate bodies on the caudal surface of the diencephalon just inferior to the caudal end of the dorsal thalamus. Its neurons project signals to both the amygdala and the higher cortical regions for further processing. Nerve fibers project out of the thalamus to the cerebral cortex in all directions allowing hub-like exchanges of informationIt has several functions such as the relaying of sensory signals including motor signals to the cerebral.
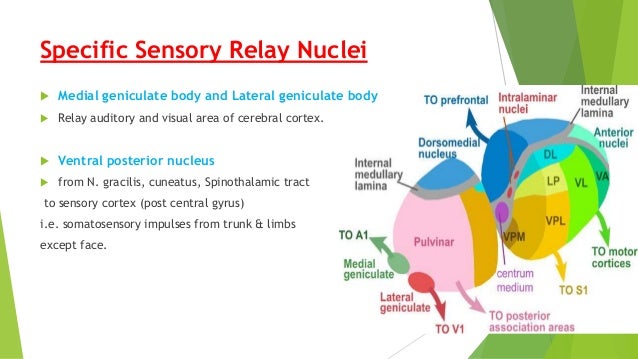
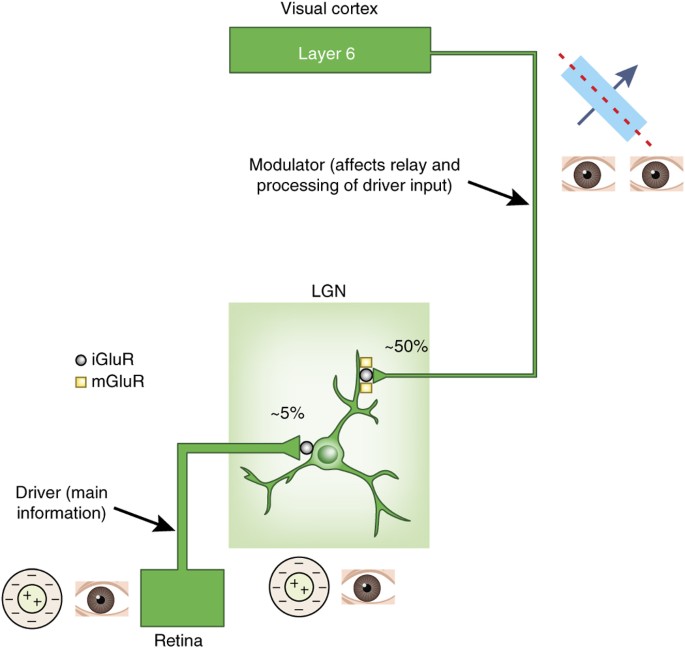
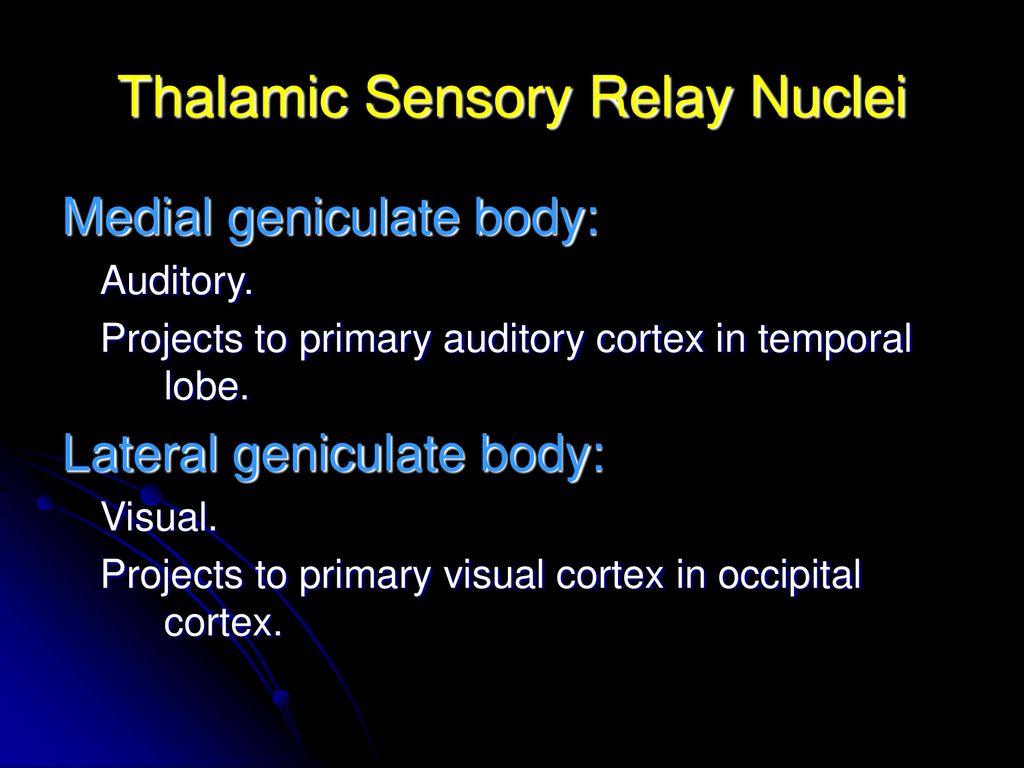
From there the small fibers rejoin the ascending reticular pathway. The medial geniculate nucleus can be subdivided into medial MGM ventral MGV and dorsal MGD subnuclei Jones 1985. The lateral geniculate nucleus LGN relays visual information including representations of location in the visual field and colour.
Activity in the developing auditory system of rodents is a composite of both sound-evoked responses and sound-independent spontaneous events that occur even before ear opening Geal-Dor et al 1993. 1 on a question The thalamic relay nucleus for the auditory system is the. Also Know where is medial geniculate nucleus.
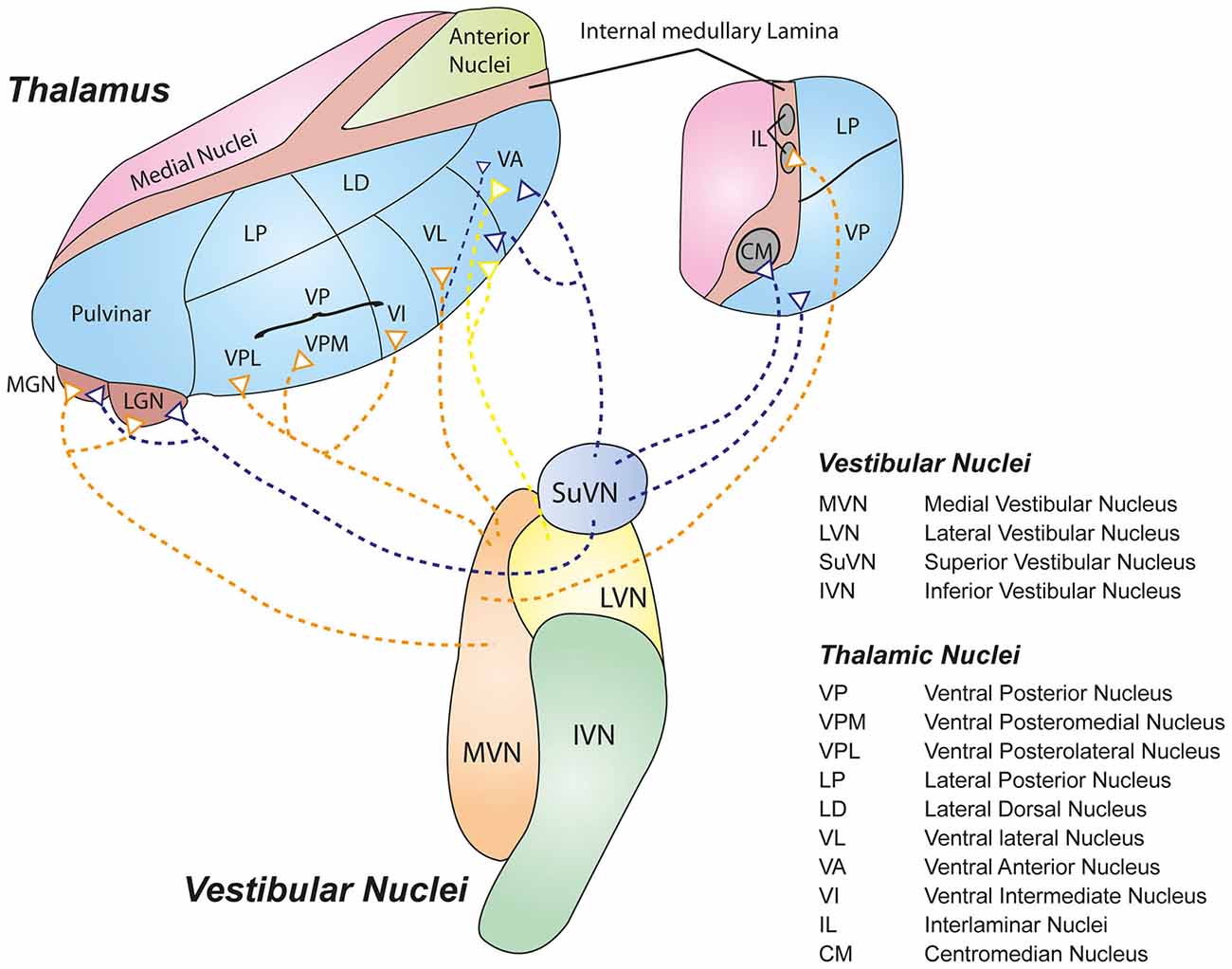
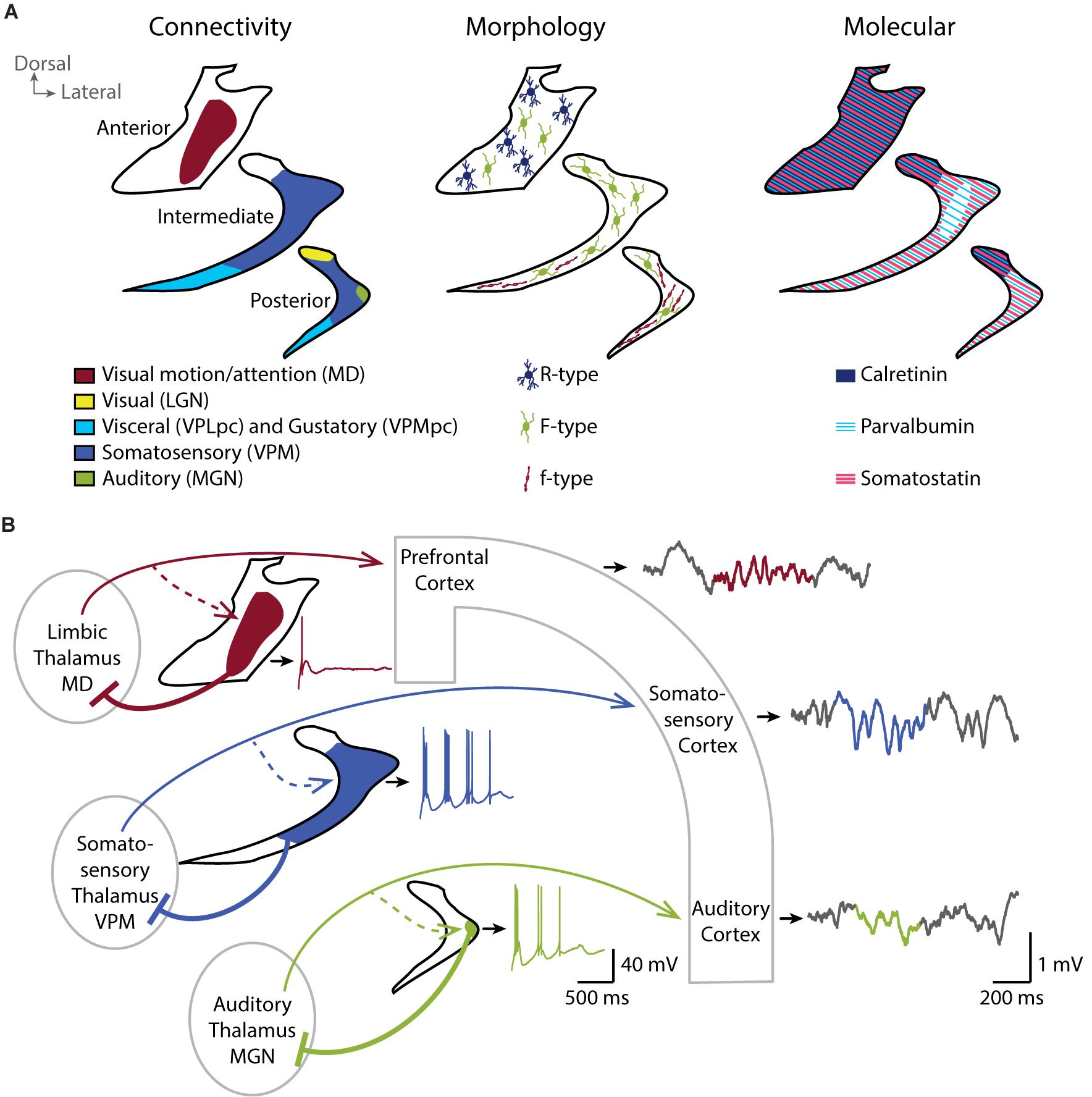
Thus visual auditory and somatosensory systems have many cortical areas22 23 24 and more than one related thalamic nucleus connected to TRN 6 9 10 11 12. This nucleus contains a high density of punctate immunoreactive structures presumed to be GABAergic axon terminals. Makarov et al 2021 spontaneous activity has been widely.
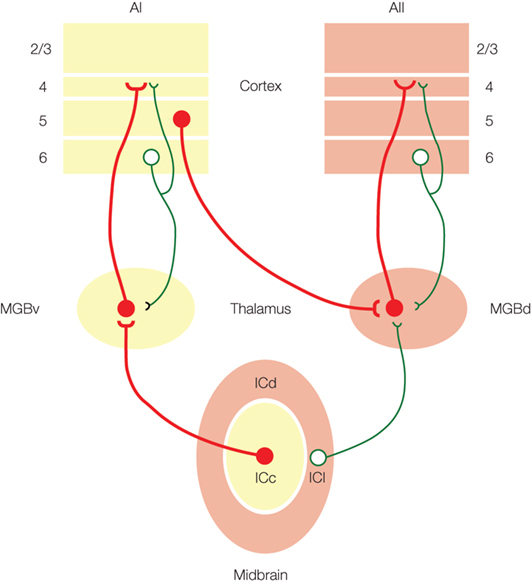
The lateral and medial geniculate bodies function as primary thalamic relay stations for. Correct answer - The thalamic relay nucleus for the auditory system is the. We used electron microscopy to determine the relative numbers of the three synaptic terminal types RL round vesicle large terminal RS round vesicles small terminal and F flattened vesicles found in several representative thalamic nuclei in cats chosen as representative examples of first and higher order thalamic nuclei where the first order nuclei relay subcortical information mainly to primary sensory.
Clerici and Coleman 1990. In contrast the thalamic relay station nucleus ovoidalis is devoid of immunostained somata.
We used electron microscopy to determine the relative numbers of the three synaptic terminal types RL round vesicle large terminal RS round vesicles small terminal and F flattened vesicles found in several representative thalamic nuclei in cats chosen as representative examples of first and higher order thalamic nuclei where the first order nuclei relay subcortical information mainly to primary sensory.
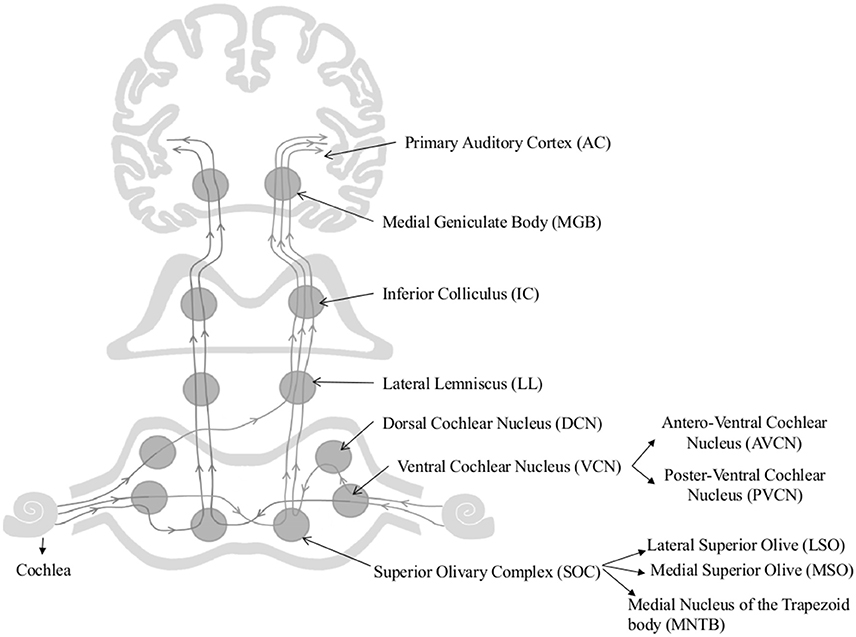
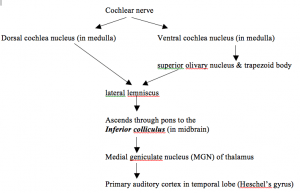
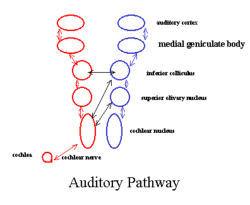
Most sensory systems are organized in a linear fashion where peripheral organ fibers project primarily through a modality-specific thalamic nucleus for example LGN for the visual system MGN for the auditory system and only then onto their respective cortical or subcortical targets. Together with the lateral geniculate body which is the relay station of the optic system it constitutes the metathalamus. Thus visual auditory and somatosensory systems have many cortical areas22 23 24 and more than one related thalamic nucleus connected to TRN 6 9 10 11 12. The lateral and medial geniculate bodies function as primary thalamic relay stations for. Nerve fibers project out of the thalamus to the cerebral cortex in all directions allowing hub-like exchanges of informationIt has several functions such as the relaying of sensory signals including motor signals to the cerebral. For any single functional thalamocortical pathway and its related TRN sector there is usually more than one connected thalamic nucleus or cortical area. Passes through inferior colliculus. The medial geniculate nucleus can be subdivided into medial MGM ventral MGV and dorsal MGD subnuclei Jones 1985. Cochlear nucleus olivary complex inferior colliculus medial geniculate auditory cortex Which of the following is the correct order of neuron layers in the retina from outermost to innermost.
In the auditory forebrain center field L and the auditory portions of the hyperstriatum ventrale up to 8 of the cells were immunopositive. The thalamus from Greek θάλαμος chamber is a large mass of gray matter located in the dorsal part of the diencephalon a division of the forebrain. The metathalamus consists of two oval eminences the geniculate bodies on the caudal surface of the diencephalon just inferior to the caudal end of the dorsal thalamus. Passes through inferior colliculus. After thalamic processing auditory projections terminate in primary. Its structures include the hypothalamus thalamus amygdala and hippocampusThe thalamus serves as a sensory relay center. The medial geniculate body MG represents the thalamic relay station of the auditory tract and thus the gateway to the centers of auditory perception in the cerebral cortex.










:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/699/HpNC4gYzPR06Aag8KW7A_thalamic-nuclei_english.jpg)





:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/medial-dorsal-nucleus/o7auT5NW8rRmaiEZlURI5g_Medial_t_nuclei_copy.png)














Post a Comment for "The Thalamic Relay Nucleus For The Auditory System Is The"